Anbieter zum Thema
Secure supply through efficient smoothing
C2 is is responsible for smoothing the output voltage. As this is a one-pulse reactance, the entire output current of C2 must be made available during the negative half-wavelength. The necessary capacitance of this depends on the permissible ripple of the output voltage. For the circuit in the example, a maximum value of 1 V is required. At the maximum load current consumption of 15 mA at 9 V, a load resistance of 600 Ω is produced. With a line frequency of 50 Hz (10 ms per half-wavelength) the minimum capacitance of C2 can thus be determined:
A single-ended aluminum electrolyte capacitor is selected with a capacitance of 150 µF and a permissible voltage of 25 VDC. In order to achieve the longest possible life, this capacitor should be designed for a temperature of at least 105 °C.
Optionally, a ceramic capacitor (C3) can additionally be connected in parallel with C2. This is used for noise suppression and for blocking voltage peaks. For example, a TDK MLCC with a capacitance of 0.1 µF can be considered for this purpose. The type C1608X7R1E104K080AA was selected with a nominal voltage of 25 VDC with size 1608 (IEC) and X7R temperature characteristic (–55 to 125 ºC, ±15%).
Circuit protection is essential
In a worst-case scenario it may happen that, when switching off without load, C1 remains charged with the peak voltage of 325 V. It is then the task of R2 to discharge the capacitor as quickly as possible. When setting the resistance value, a compromise must be made between power dissipation and discharge time constant. In this case the value of 470 kΩ was selected. A power dissipation of approx. 0.1 W occurs here and the discharge time to a maximum permissible touch voltage of 50 V takes around 0.5 s. If the power supply is continuously connected to the grid, however, there is no need for this resistor.
The overvoltage protection at the line input (RV1) is also important, of course. For this purpose, TDK offers various series of EPCOS varistors. The types from the EPCOS standard series are suitable for the stated circuit, as these cover a wide range of voltages from 11 VRMS to 1100 VRMS. These protection components are available with disk diameters of between 5 mm and 20 mm, corresponding to the required surge current capability and energy absorption. In this case, for example, the compact type B72205S0231K101 with a disk diameter of 5 mm is suitable, which features a surge current capability of 400 A at a pulse of 8/20 µs.
In addition, the output of the circuit can also be protected against overvoltage (RV2), for example, using the EPCOS SMT CeraDiode B72590D0150A060, which has a DC voltage of 15 V.
Finally, an EPCOS PTC B59873C0120A570 (RT1), which is designed for a maximum load current of 90 mA at 25 °C, ensures the current limitation at the power input. If a fault should occur in the circuit that results in an increased current flow, the PTC heats up, causing its resistance to rise sharply and thus limit the current to non-critical values.
* Christoph Jehle is Manager Product Communications at TDK in Munich.
(ID:43634765)





:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/f4/ca/f4ca5350a448ca833cd05e87703019d6/0128902853v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/ea/2a/ea2a033222605e608a8121bf90cb04c8/0128893388v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/89/6d/896df53a45806826443c1d4b7b954992/0128555431v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/7d/bb/7dbb06378b5a3d4cf0a96a9ea38a0261/0128880826v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/df/09/df09d635cf5ff7dbdd503a559274dadc/0128886473v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/9d/55/9d551aa422d51c415628a615dfad47b1/0128886693v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/38/10/3810d163ae77015a84eb8d9e0ccdb3f2/0128871470v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/d8/80/d880f26a5e6b9488861f1d713f085023/0128847366v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/00/cf/00cfd71f9b1e00f7d572558ae654362e/0128838981v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/d6/cf/d6cf6e7d535319f6c7b80c0196c06780/0128790900v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/46/95/4695fb8b40fad52300436b044da4ea67/0128770184v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/6e/67/6e67b8257b53970fc9bac7f09d9f5afe/0128880777v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/48/30/48309116c311427f0604cda4fcb92b26/0128891078v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/7f/a6/7fa68cc7dbda0e40809e6ec2a064d3a9/0128830887v3.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/9c/35/9c35ed04fa562b190cbc496a695a6802/0128823288v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/d7/e6/d7e6fe4124ec2efc726e9c3f2c2a4cfc/0128241940v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/7d/68/7d68aecf780e15057f14df63731fb935/0127934402v3.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/ec/ad/ecad1a990fb931892757865d0270eabb/0127959299v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/d0/31/d0318b5503cd12a34eef53941547fff8/0128912090v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/d4/ff/d4ffb5ae3f9a2d9755b395cfe082d391/0128875656v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/52/bb/52bbdf63addc5652d9fc2f8908124327/0128808573v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/65/a2/65a2ec3da11379e70bf8933d1170353c/0128776801v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/c7/2f/c72f9de0f70aa2e496a4001d4267032a/0128804348v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/32/93/3293abe43d16822fba0c2f7b16ebf84e/0128782553v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/45/fe/45feae490305c591ce1428c2e13cc34c/0128897569v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/2a/2c/2a2c4d29a353c1aa8abc39c5ddf6c96b/0128894213v3.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/ee/0f/ee0f3ba5bbfdcf51a749a3844f59320c/0128870257v3.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/d9/6d/d96dfa3d82837cca1dc111b292abba9a/0128893036v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/64/63/6463f6d5382f7deb935d82c0a23acbfe/0128885787v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/69/1f/691f39ba12be3cad90eb88bdabc456a6/0127321404v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/6a/cc/6acc4f803241cfe5b6d60560c0a2b4d9/0126684948v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/ef/aa/efaae5a25fb0a4c55c434611033447af/0126532350v2.jpeg)
:fill(fff,0)/images.vogel.de/vogelonline/companyimg/76800/76895/65.jpg)
:fill(fff,0)/images.vogel.de/vogelonline/companyimg/130400/130457/65.jpg)
:fill(fff,0)/p7i.vogel.de/companies/67/8a/678a0c5c3e273/logo-caltest-instruments-signet.png)
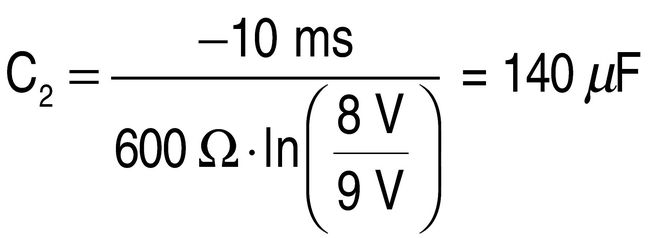
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/da/e4/dae45caa7f4fa7125e17b07d9da016bb/0125786170v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/7d/27/7d277a20a9ea7e17c226372c4d951316/0124246561v2.jpeg)